Versions
Massdriver uses semantic versioning (SemVer) to manage bundle versions and deployments. This provides predictable versioning behavior and enables sophisticated release management workflows that automate infrastructure updates across your environments.
Versions is currently in prerelease schedule to be publicly available Nov 7th. If you would like to be opted in please post a message in the community support channel or from the support chat while logged in to Massdriver.
Semantic Versioning
All bundle versions in Massdriver follow the semantic versioning specification MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH:
- MAJOR: Incremented for incompatible API changes
- MINOR: Incremented for backwards-compatible functionality additions
- PATCH: Incremented for backwards-compatible bug fixes
Examples
1.0.0 # Initial release
1.0.1 # Patch release (bug fixes)
1.1.0 # Minor release (new features)
2.0.0 # Major release (breaking changes)
Development Releases
Development releases allow you to test versions before they become official releases. They use the format MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH-dev.TIMESTAMP:
1.2.0-dev.20060102T150405Z # Development release for 1.2.0
1.2.0 # Final release
Key Properties
- Ordering: Development releases are sorted before their corresponding release version
- Testing: Perfect for staging environments and pre-production testing
- Timestamps: Multiple development releases are ordered by timestamp (higher = newer)
Rapid Infrastructure Testing
Development releases are a powerful means of rapidly testing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) changes against real cloud resources:
Local Development + Real Infrastructure:
- Develop bundle changes locally on your machine
- Publish development releases without affecting production bundles
- Deploy development releases to real cloud environments for comprehensive testing
Opt-in Testing Network:
- Set up multiple packages using release channels with "Enable Development Releases" toggle
- These packages automatically pick up your latest development releases and run the full deploy/apply pipeline
- Run Terraform plans and compliance scans against actual provisioned resources
- Validate infrastructure changes with real cloud provider APIs
Practical Workflow:
# 1. Make IaC changes locally
vim src/main.tf
# 2. Publish development release for testing
mass bundle publish --development
# 3. Visit the output URL to monitor all test infrastructure
# 4. Watch plan/apply/compliance pipelines execute automatically
# 5. Review Terraform plans and compliance results from real infrastructure
# 6. Iterate with new development releases or publish final release
This approach lets you stand up multiple real-world examples of your infrastructure changes before committing to a final release, ensuring your bundles work correctly across different cloud environments and configurations.
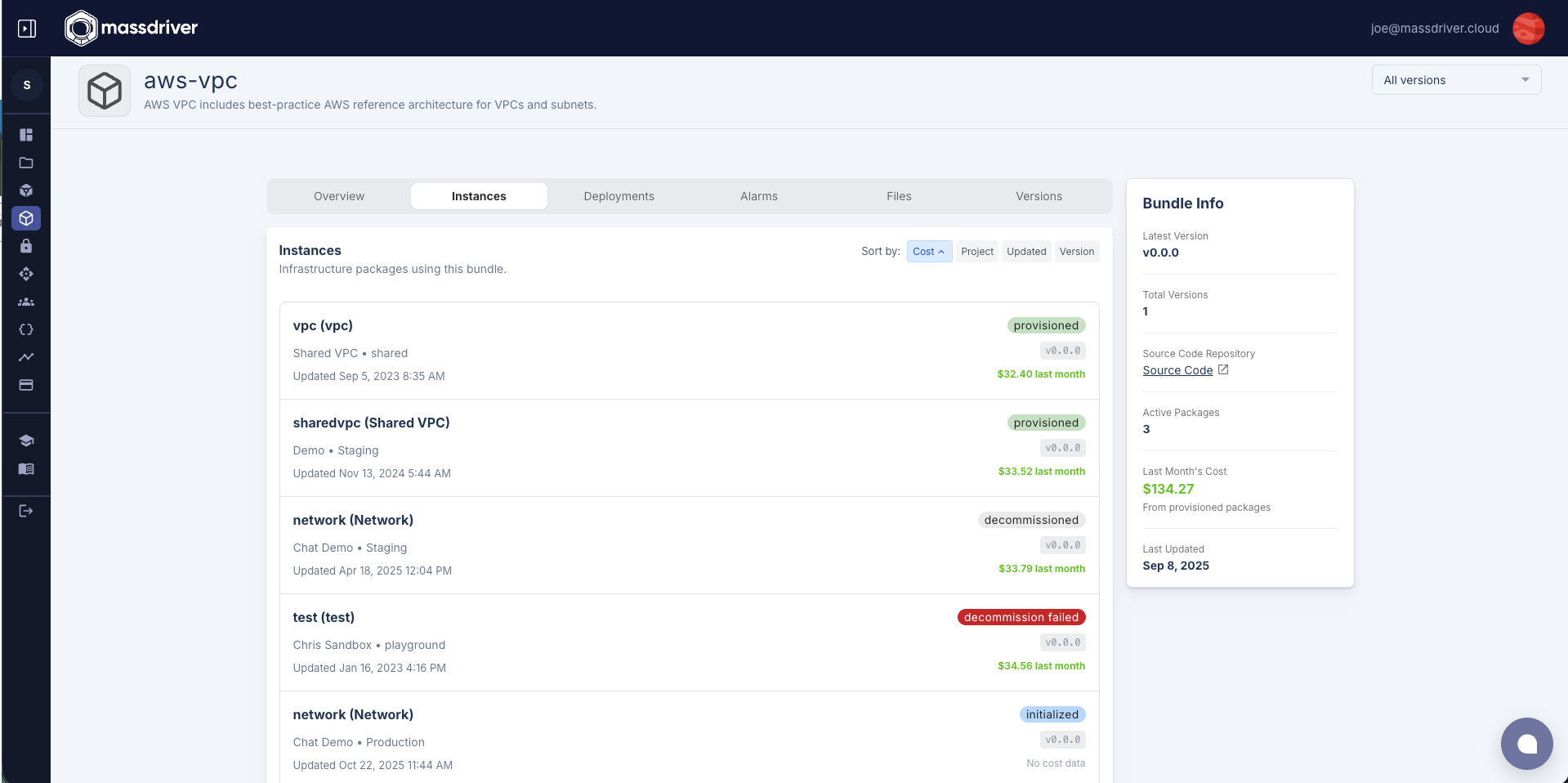
Release Channels
Release channels use tilde (~) constraints to specify compatible version ranges. When a package uses a release channel, it automatically runs the full deploy/apply pipeline whenever a new version matching that channel is published. This includes compliance checks, Terraform plans, and all other validation steps. This automates infrastructure version management.
Major Channel (~1)
Matches the latest version within major version 1:
~1could resolve to1.5.3(latest in major 1)- Will not upgrade to
2.0.0 - Automatically deploys when new minor or patch versions are published (e.g.,
1.6.0,1.5.4)
Minor Channel (~1.1)
Matches the latest patch within minor version 1.1:
~1.1could resolve to1.1.7(latest patch in 1.1.x)- Will not upgrade to
1.2.0 - Automatically deploys when new patch versions are published (e.g.,
1.1.8)
Latest Channel (latest)
Matches the newest stable release:
- Will return the highest semver version, not "most recent"
- Will upgrade to any newer stable version
- Automatically deploys when any new stable version is published
Release Strategies
Stable (Default):
- Only receives stable releases
- Excludes development releases
- Recommended for production environments
Development Release:
- Receives both stable and development releases
- Automatically includes development releases when using release channels
- Recommended for testing and staging environments
Development Releases and Real Infrastructure Testing
Development releases let you test infrastructure changes against actual cloud resources before promoting a version to release. Publishing a development release outputs a monitoring URL for every package configured to test it. These packages automatically deploy the development release and run their full validation pipeline—Terraform plans, compliance checks, and deployments—against live cloud APIs.
This process validates infrastructure changes across multiple environments and configurations simultaneously, revealing issues like API drift, quota limits, and provider-specific behaviors that static analysis tools can't catch.
Automated Version Distribution with Release Channels
Release channels automate version distribution across environments. Instead of updating every package manually, you publish once, and packages automatically upgrade based on their configured version constraints.
For example, a package on channel ~2.5 will automatically deploy any patch release (2.5.1, 2.5.2, etc.), while staging or dev environments may use wider channels for faster updates. This keeps environments current within defined boundaries and ensures security patches flow automatically—without coordination or manual promotion steps.
Version Management in Massdriver
Bundle Development and Publishing
Setting Bundle Version
In your massdriver.yaml, you now specify a version field:
schema: draft-07
name: aws-rds-postgres
description: "PostgreSQL database on AWS RDS"
version: "1.2.3" # Must be valid semantic version
Version Rules:
- Required Format: Must be
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH(e.g.,1.2.3) - Default Fallback: If omitted, defaults to
0.0.0(for backwards compatibility) - Immutable Releases: All versions are immutable once published, except
0.0.0- Version
0.0.0can be republished multiple times - This allows teams to iterate and work through an initial release without version management overhead
- Once you publish any other version (e.g.,
0.0.1or1.0.0), it becomes immutable
- Version
Publishing Options
Standard Release:
mass bundle publish
- Publishes the exact version from
massdriver.yaml - Creates an immutable release
- Available immediately for use by your end users
Development Release:
mass bundle publish --development
# or
mass bundle publish -d
- Adds
-dev.TIMESTAMPto your base version (e.g.,1.2.3-dev.20060102T150405Z) - Base version (
1.2.3) must not have been published yet - Allows testing before the final release
- Perfect for feature branches and testing workflows
- Outputs a URL to view all test infrastructure using this development release
- See plan/apply/compliance pipelines executing in real-time
- Monitor all packages configured to test this development release
Package Version Management
Version Selection Interface
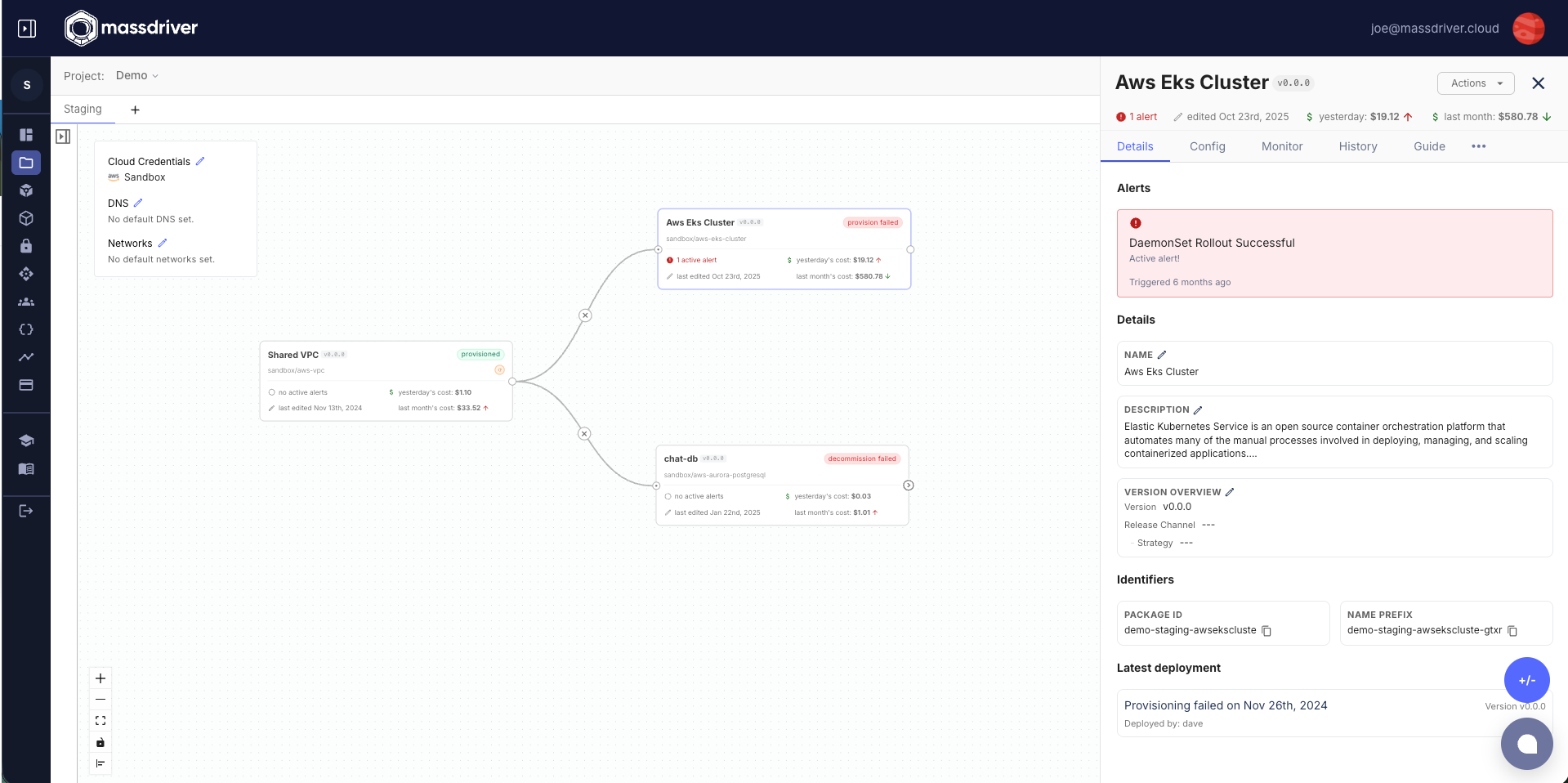
In the package configuration panel, developers can set the version constraint:
Published Versions (Strict SemVer):
1.0.0,1.1.0,1.1.5,2.0.0(exact published versions only)- Not free-form - must select from published versions
- Development releases are hidden from this interface
Generated Release Channels:
~1,~1.1,~2,~2.1(auto-generated tilde patterns for each possible)latest- Newest SemVer release- When you set a version constraint,
resolvedVersiongets updated to show what will deploy
Version Constraints
Upgrade-Only Policy:
- ✅ Can upgrade:
1.0.0→1.1.0→2.0.0 - ❌ Cannot downgrade:
2.0.0→1.1.0 - ✅ Can rollback: Restore previous configuration with its original version
Configuration Snapshots: Each version change creates a configuration snapshot, enabling safe rollbacks to previous states while maintaining the upgrade-only constraint for new deployments.
Upgrade Strategies
Feature Upgrades
Use minor channels for patch updates:
~1.1 # Patch updates only (1.1.0 → 1.1.5)
Major Upgrades
Use major channels for latest features:
~1 # All updates within major 1 (1.0.0 → 1.9.5)
Best Practices
For Bundle Developers
Set Explicit Versions: Always specify
versioninmassdriver.yamlversion: "1.2.3" # Explicit semantic versionDevelopment Workflow: Use development releases for testing
# Set version in massdriver.yaml
version: "1.5.0"
# Publish development release for testing
mass bundle publish --development # Creates 1.5.0-dev.timestamp
# Outputs URL to view all test infrastructure and pipeline executions
# Monitor plan/apply/compliance pipelines in real-time
# Publish final release
mass bundle publish # Creates 1.5.0Follow SemVer Guidelines:
- Patch (
1.0.1): Bug fixes, security updates, documentation - Minor (
1.1.0): New optional features, additional cloud regions - Major (
2.0.0): Breaking changes, removed parameters, incompatible updates
- Patch (
Version Progression: Ensure each version is greater than the previous
- ✅
1.0.0→1.0.1→1.1.0→2.0.0 - ❌ Don't skip versions unnecessarily
- ✅
Version Lifecycle
Workflow Steps:
- Version Definition: Set semantic version in
massdriver.yaml - Development Release: Optional development release publishing for testing (
-dflag) - Testing Phase: Validate development releases in staging environments
- Stable Release: Publish final immutable version
- Package Selection: Choose version strategy in UI dropdown
- Deployment: Package runs with selected version/automation rule
Version Fields and Properties
Each package in Massdriver has several version-related fields that control how it behaves:
Package Version Fields
version- The version constraint (e.g.,"1.2.3","~1.2","latest")releaseStrategy- Whether the package receivesstablereleases only or alsodevelopmentreleasesresolvedVersion- The resolved semantic version that will be deployed nextdeployedVersion- The version that was last successfully deployed to infrastructureavailableUpgrade- The newest version available for upgrade based on the constraint