Setup Access with KubeConfig and Kubectl
This guide will cover how to access your Kubernetes cluster using a kubeconfig file and a tool called kubectl.
Prerequisites
- A running Kubernetes cluster in Massdriver (AKS, EKS, or GKE)
- kubectl installed
Downloading your kubeconfig file
- In Massdriver, navigate to the Kubernetes cluster you want to access
- Click on the deployment and open the
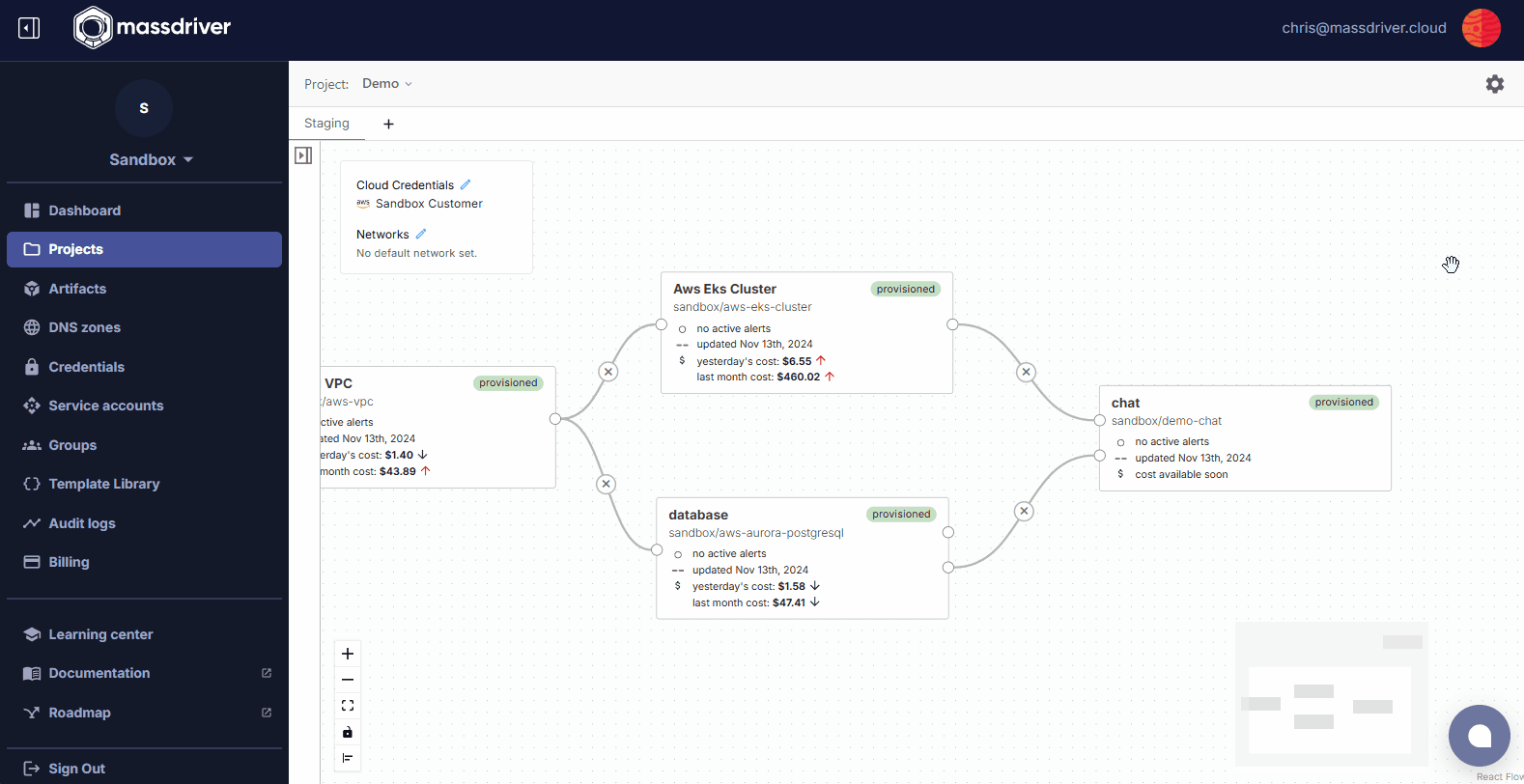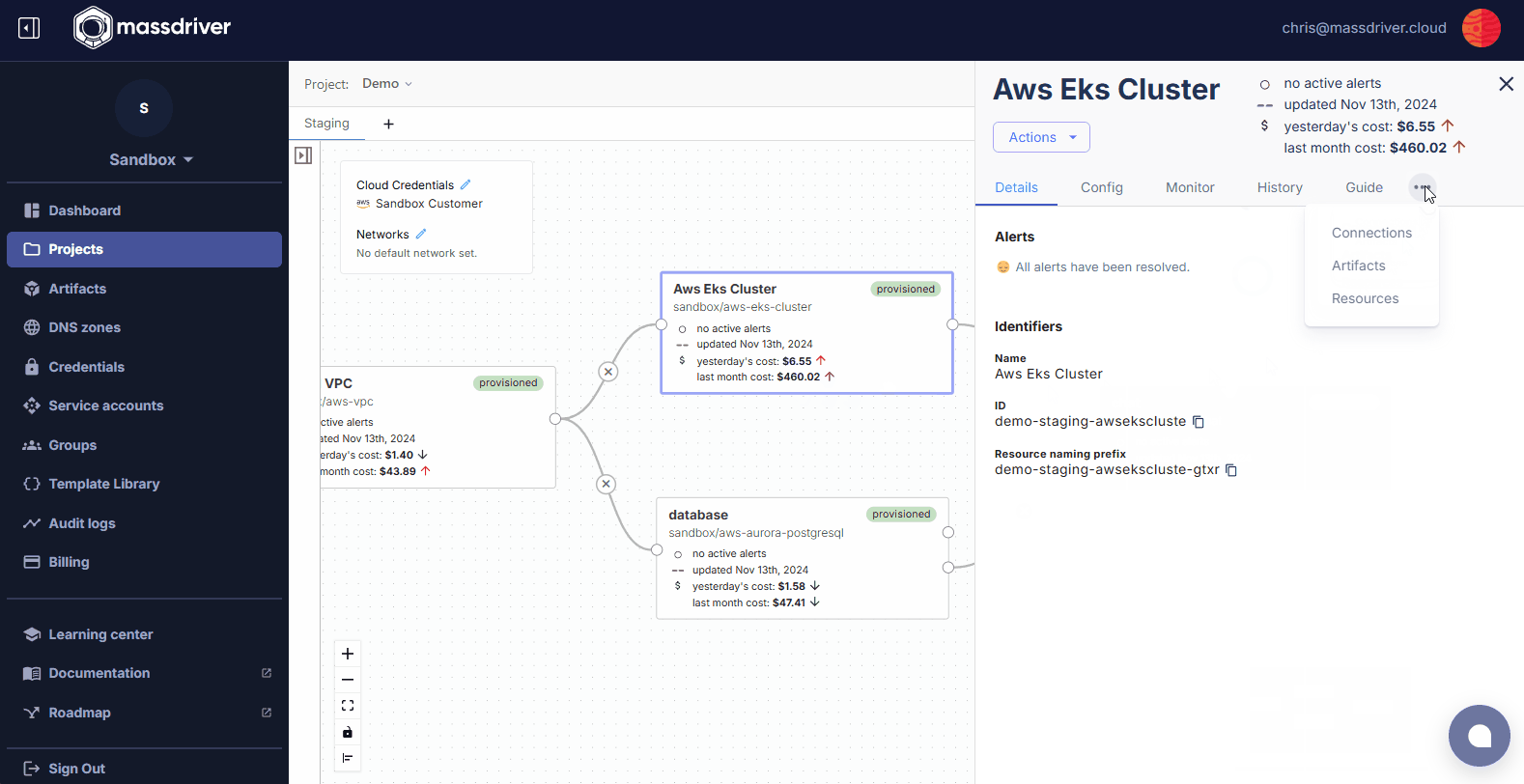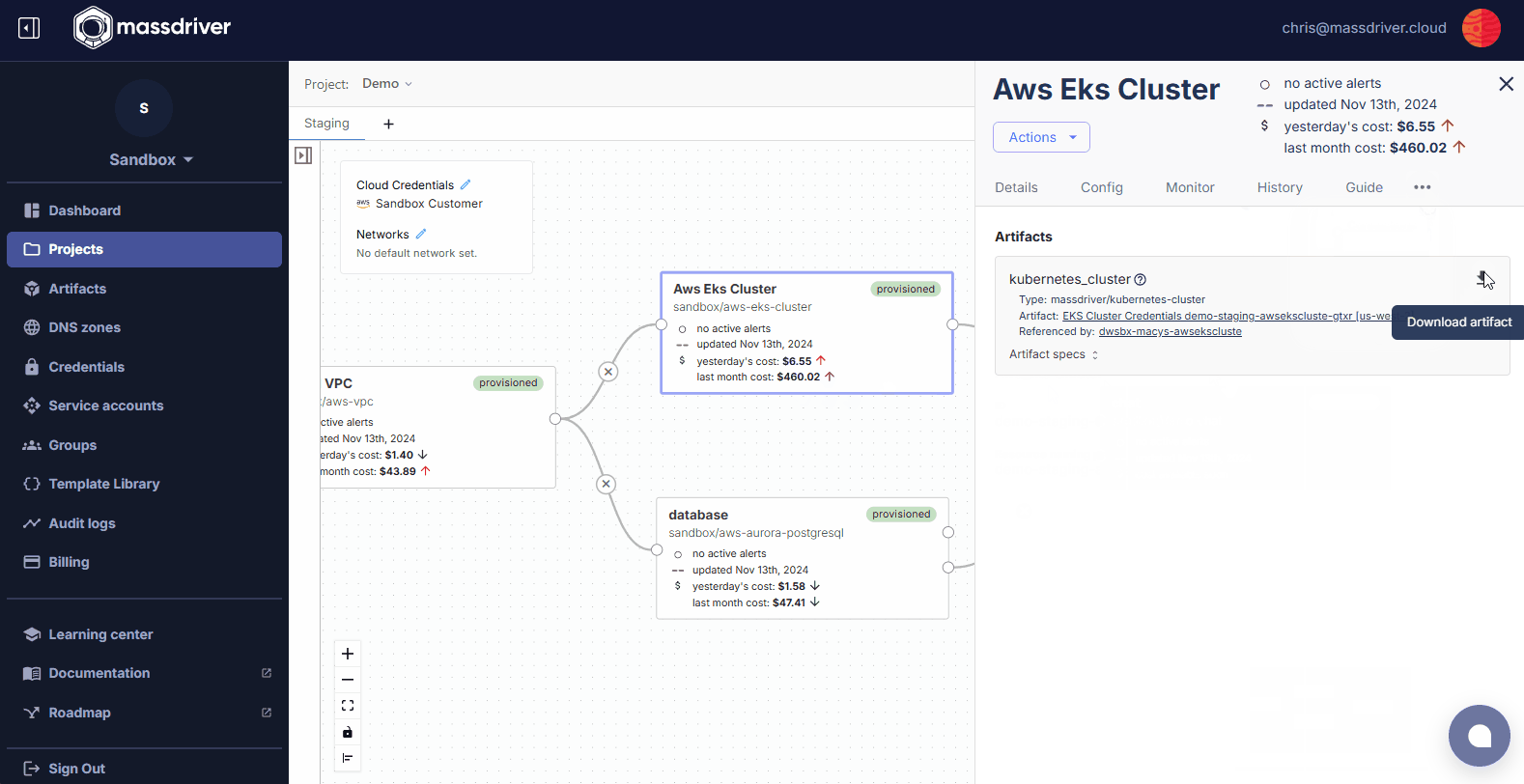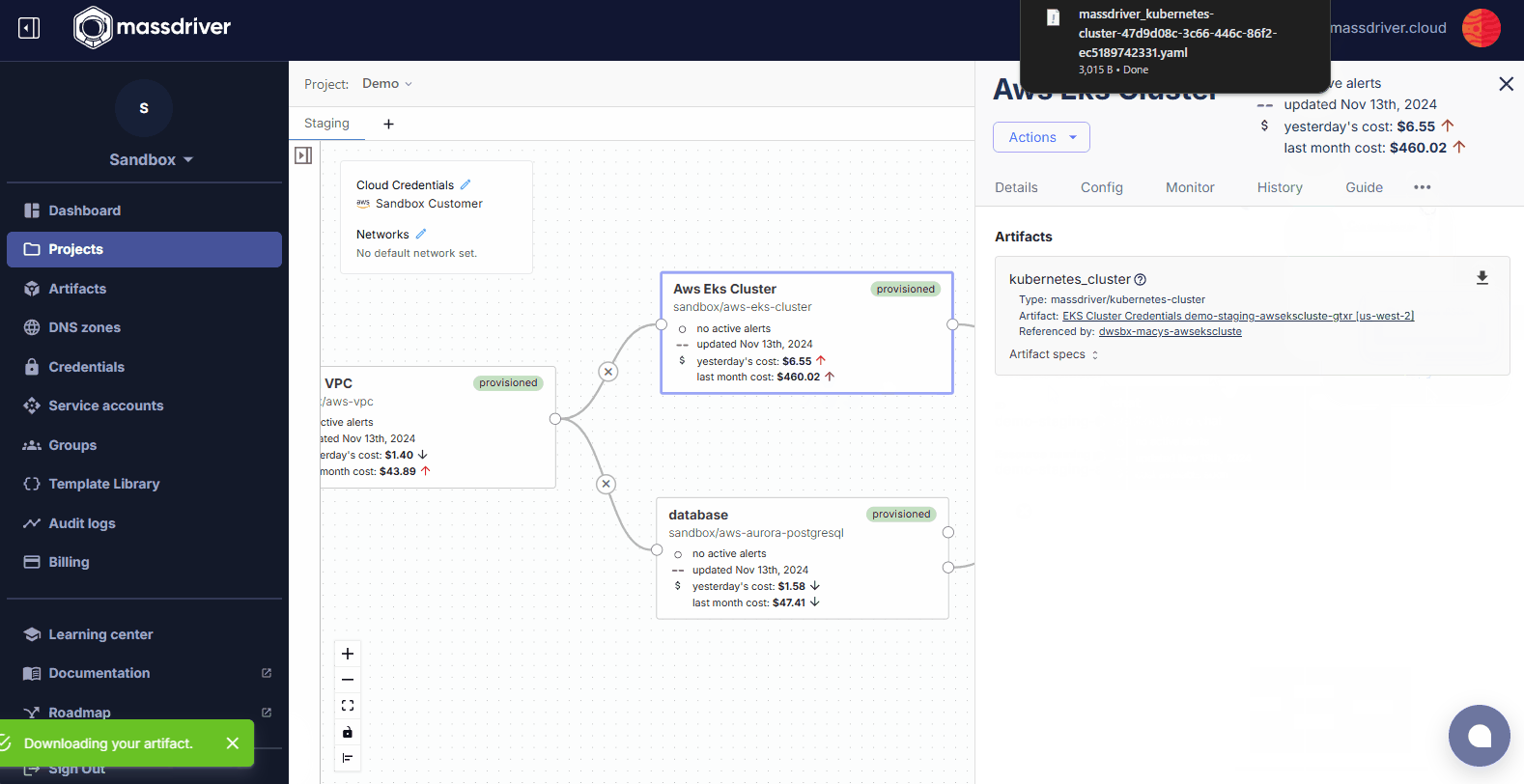
Artifactstab - Click the download button and then click
Kube Config
Setting KUBECONFIG environment variable
note
By default, kubectl looks for a file named config in the $HOME/.kube directory. If you want to use a different kubeconfig file, you can specify it using the KUBECONFIG environment variable.
Move the downloaded kubeconfig file to a location of your choice (preferably in the
$HOME/.kubedirectory)In your terminal, set the
KUBECONFIGenvironment variable to the path of the downloaded kubeconfig file
export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/kubeconfig.yaml
You can also specify other kubeconfig files by setting the --kubeconfig flag for kubectl commands.
Basic commands
Get cluster information
General:
kubectl get namespaces # Lists all namespaces
kubectl api-resources # Lists all resources in the cluster
Pods:
kubectl get pods # Lists all pods in default namespace
kubectl get pods -n <namespace> # Lists all pods in a specific namespace
kubectl get pods -A # Lists all pods in all namespaces
kubectl get pods -w # Watches for changes to pods
kubectl get pods -o wide # Lists pods with more information
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> # Describes a specific pod
kubectl top pod <pod-name> # Shows CPU and memory usage of a specific pod
kubectl logs <pod-name> # Shows logs of a specific pod
kubectl logs -f <pod-name> # Shows logs of a specific pod and follows the logs
Services:
kubectl get services # Lists all services in default namespace
kubectl get services -n <namespace> # Lists all services in a specific namespace
kubectl describe service <service-name> # Describes a specific service
Nodes:
kubectl get nodes # Lists all nodes
kubectl describe node <node-name> # Describes a specific node
Deployments:
kubectl get deployments # Lists all deployments in default namespace
kubectl get deployments -n <namespace> # Lists all deployments in a specific namespace
kubectl describe deployment <deployment-name> # Describes a specific deployment
Accessing cluster resources
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- sh # Executes a shell in a specific pod
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- env # Prints environment variables of a specific pod
kubectl port-forward <pod-name> 8080:80 # Forwards a local port to a port on a specific pod
kubectl apply -f <file.yaml> # Applies a configuration file to the cluster