Create
Before getting started you'll need:
- Massdriver CLI
- Service Account key
- A containerized application. Quick start application examples are available here.
In this guide we'll generate an application bundle and publish it to Massdriver. The application bundle will be all of the configuration your application needs to connect to runtimes (serverless, containers) and cloud resources (queues, databases, etc). Once the application bundle is published, we'll configure it in the UI and set up continuous deployments from GitHub actions.
First, create a new application bundle:
mass bundle new
Enter k8s-phoenix-chat-example as the name and a description. These will be used in the Massdriver UI to identify application bundles to users.
We recommend prefixing application and infrastructure bundles with where they run (i.e: k8s-) to guide users in selecting the right bundle.
Name: k8s-phoenix-chat-example
Description: A phoenix chat app
Next an application template will need to be chosen.
For this example we'll choose kubernetes-deployment:
? Template:
aws-lambda
azure-function
kubernetes-cronjob
▸ kubernetes-deployment
kubernetes-job
Application templates are cached locally the first time mass bundle new is run. To get the latest application templates run mass app template refresh.
Then, connections (your application dependencies) will need to be selected.
For this example we'll choose massdriver/postgresql-authentication.
? What connections do you need?
If you don't need any, just hit enter or select (None)
[Use arrows to move, space to select, <right> to all, <left> to none, type to filter]
[ ] (None)
[ ] massdriver/aws-dynamodb-table
...
[ ] massdriver/mongo-authentication
[ ] massdriver/mysql-authentication
> [ ] massdriver/postgresql-authentication
[ ] massdriver/redis-authentication
You'll be prompted to name the variable for each connection that you added. We suggest simple names like postgres, but if you have more complex dependencies it may make sense to use names like inventory_database for an inventory database or website_cache for a Redis website cache.
Finally, you'll be prompted for the output directory. There are different schools of thought as to if your application's cloud configuration should be stored alongside your application code or in a different directory. For private applications, we suggest keeping it alongside your application code to simplify CI/CD.
For this example we'll set the output directory to k8s-phoenix-chat-example since we are using a publicly available application and docker image.
Files in the Application Bundle
The following directory structure will be created:
massdriver.yaml- Bundle metadata, input parameter requirements / validation, connections / dependencies, and UI controlssrc- Infrastructure-as-code rigging for your application. This will generally be the IAM, observability, and deployment configuration of your app.README.md- It's a README 🤓
The massdriver.yaml is covered in detail in the Bundle YAML Specification.
It's important to note that the generated code is a great way to get started, but you can customize the fields in massdriver.yaml and the rigging code in src to meet your needs.
In this example, we generated a Kubernetes deployment with a Helm chart. The generated Helm works well for most deployments, but you can replace or edit the chart as necessary. The values provided at provisioning time will be passed in similarly to values.yaml in a standard Helm chart.
Configuring Apps
In addition to the configuration options exposed in the bundle guide, two additional configuration options are exposed to application bundles:
app.envs- Map of environment variables to set on the running application.app.secrets- Map of secret definitions. These will be presented in your application's configuration interface in Massdriver and can be set per-package or for preview environments.
Both of these configuration options expect jq queries to extract values from parameters or upstream connections.
Environment Variable Examples
Environment variables can be extracted from parameters and/or connections. Massdriver parses jq expressions to allow for rich composition of values into environment variables:
The following would set the LOG_LEVEL in your application based on the value a users selects from the log_level dropdown.
The .params prefix tells Massdriver where to pull the value from. The field names can be any complex expression with JQ as we'll see in the next example.
app:
envs:
LOG_LEVEL: .params.log_level
PORT: .params.port | tostring
Here we set the POSTGRES_USERNAME to the username field in our Postgres connection's authentication object.
app:
envs:
POSTGRES_USERNAME: .connections.postgres.data.authentication.username
While secrets are automatically converted to environment variables, they can also be parsed if necessary. More on secrets below.
The structure of each artifact type is documented here.
In the following example we compose all of the components of the Postgres authentication object into a POSTGRES_URL environment variable.
app:
envs:
POSTGRES_URL: '@text "postgres://" + .connections.postgres.data.authentication.username + ":" + .connections.postgres.data.authentication.password + "@" + .connections.postgres.data.authentication.hostname + ":" + (.connections.postgres.data.authentication.port|tostring) + "/chat?sslmode=disable"'
Secret Examples
Secrets can be defined in your massdriver.yaml file. This will create forms in the Massdriver UI where 3rd party secrets can be set for your application.
Secrets will be turned into environment variables at deploy time and are also exposed to the envs section for JQ parsing similar to .params and .connections above.
app:
envs:
FOO: bar
# SOME_SECRET is automatically created, but if you needed to map to a different var or perform parsing on the secret, you can do so
SOME_SECRET_RENAMED: .secret.SOME_SECRET
SOME_SECRET_UPCASED: .secret.SOME_SECRET | ascii_upcase
secrets:
SOME_SECRET: # This is env var name this will be converted to
required: true # if a secret is required, Massdriver will block deployments that are missing this secret
title: "A nice name for the UI"
description: "A great description for the UI"
Parameters
The params in your massdriver.yaml are really good defaults for a Kubernetes deployment. Feel free to add or remove values depending on what you want to expose to your users / developers.
With Helm-based applications the values.yaml file will be loaded as the base level defaults, and your parameters will be applied on top of those. If there are parameters that you don't want exposed to end users, simply remove the parameter from params and add the hard coded value to the values.yaml file.
A good example of where to do this is your container repository (.params.image.repository). For private applications it may make sense to hard code this value to something like my-org/web-api. You could remove this field and set the image repository manually in the values.yaml file.
To run this example, we'll set the default for the image.repository.
# under params.properties.image.properties:
repository:
title: Repository
default: massdrivercloud/phoenix-chat-example
The repository is available here and the code is on GitHub.
Connections
Your generated connections should resemble those below. In this example we have two required connections:
kubernetes_cluster- the cluster the app will deploy topostgres- the database the app needs
Additionally there are a few optional cloud authentication mechanisms. This bundle will use whichever cloud is connected in the UI to create IAM roles and permissions for your application.
connections:
required:
- kubernetes_cluster
- postgres
properties:
kubernetes_cluster:
$ref: massdriver/kubernetes-cluster
aws_authentication:
$ref: massdriver/aws-iam-role
gcp_authentication:
$ref: massdriver/gcp-service-account
azure_authentication:
$ref: massdriver/azure-service-principal
postgres:
$ref: massdriver/postgresql-authentication
If you followed the prompts in this guide, you should end up with an application bundle that looks like this.
At this point the application bundle can be published to the Massdriver bundle manager:
mass bundle publish
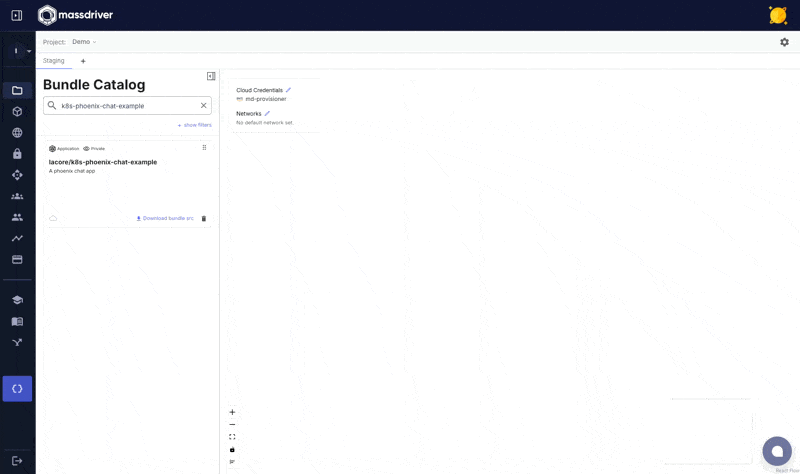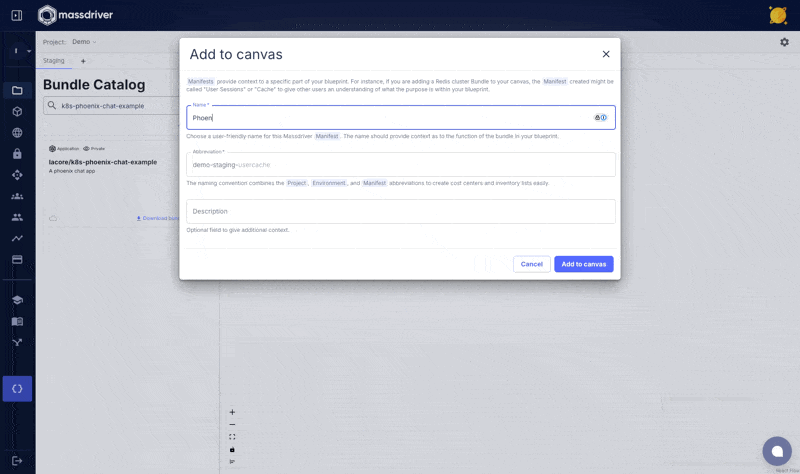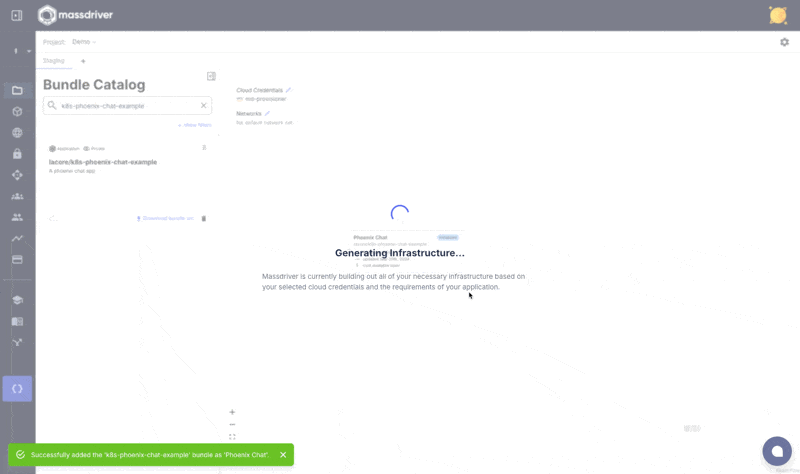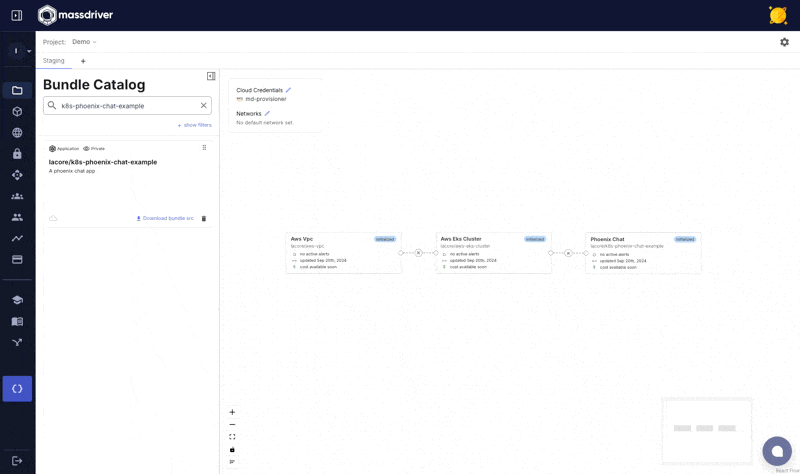
You should see a success message. Upon visiting a project canvas in Massdriver, your k8s-phoenix-chat-example should be visible in the bundle bar prefixed with your organization name.
Add Kubernetes and Postgres to your canvas, connect, and deploy!
If you would like to automatically publish your application bundle in CI/CD, see the GitHub Actions guide.
We have a number of pre-defined application templates available here. We welcome PRs to add more.