Deploy
Once an application bundle has been published to Massdriver, it can be connected and configured via the UI and then deployed via UI or CLI.
From the UI, you can deploy any application you have access to which includes your private applications and public open-source applications added by the community.
To finish this guide you will need:
- A connected cloud (AWS, Azure, or GCP)
- A domain name registered with your cloud
- A Service Account
Log into Massdriver.
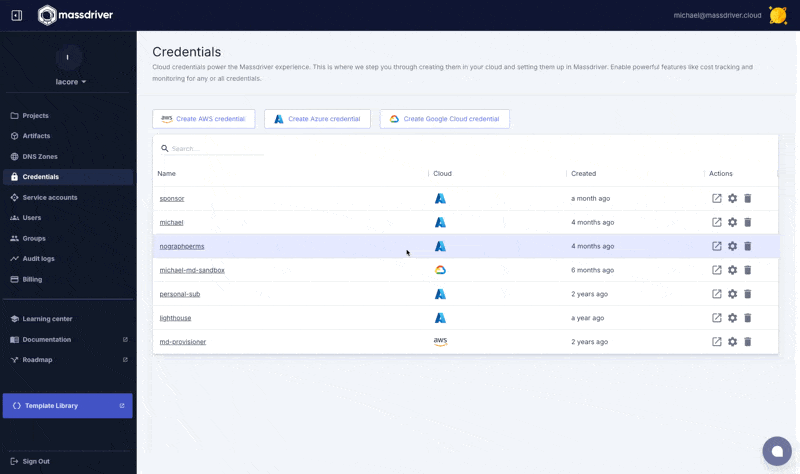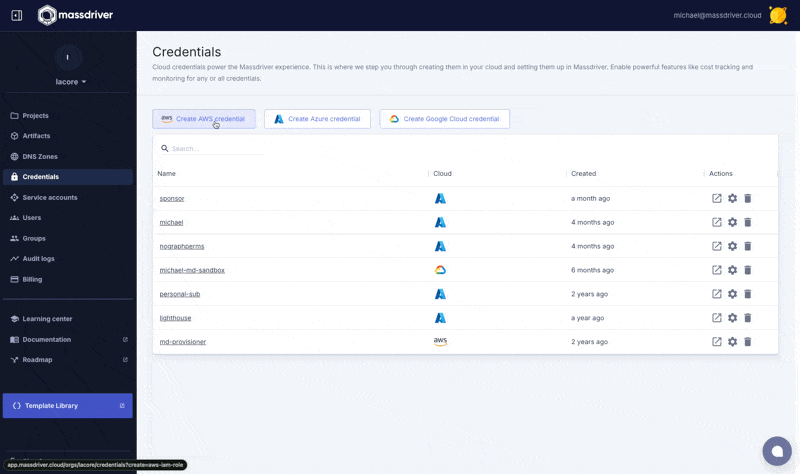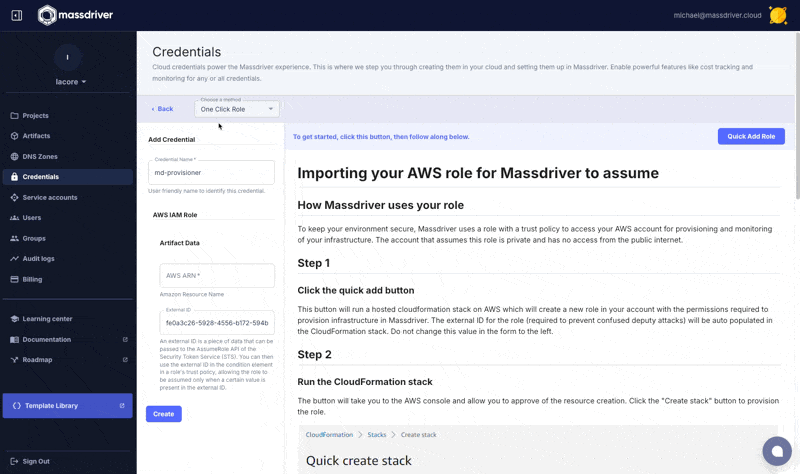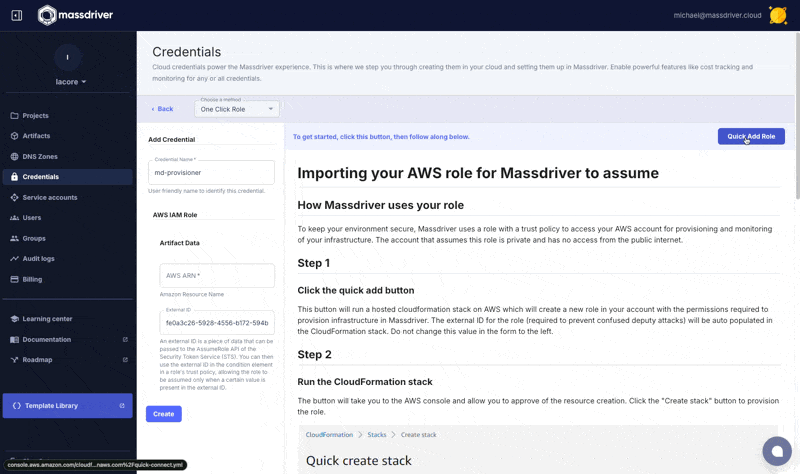
Navigate to Organization > Credentials and click Create AWS credential and follow the instructions on the screen.
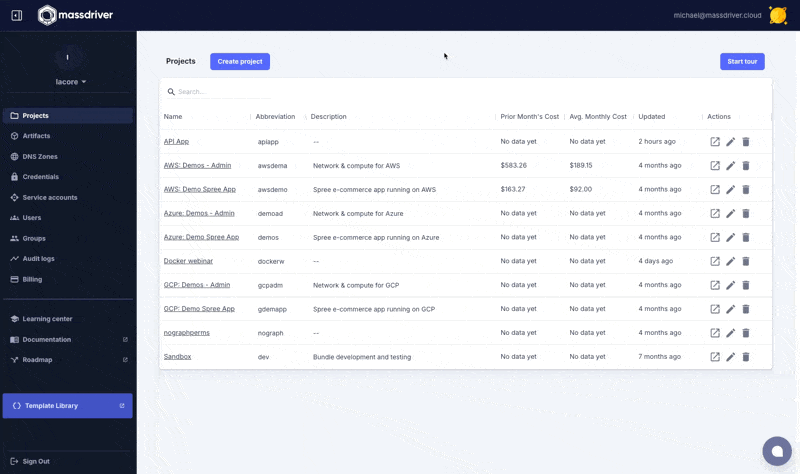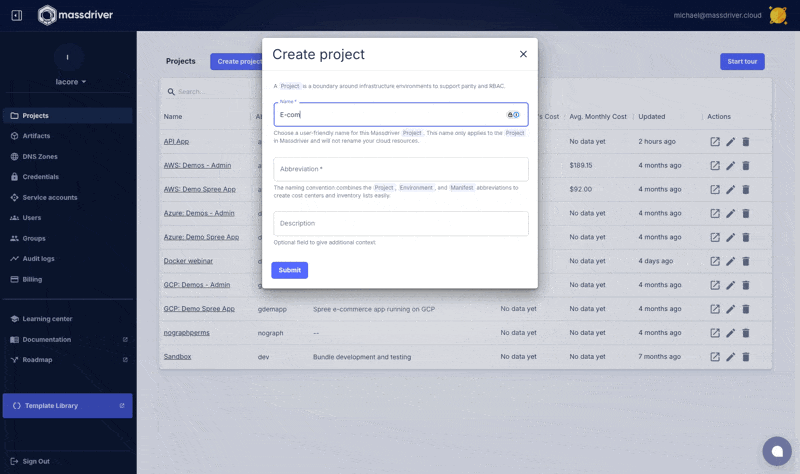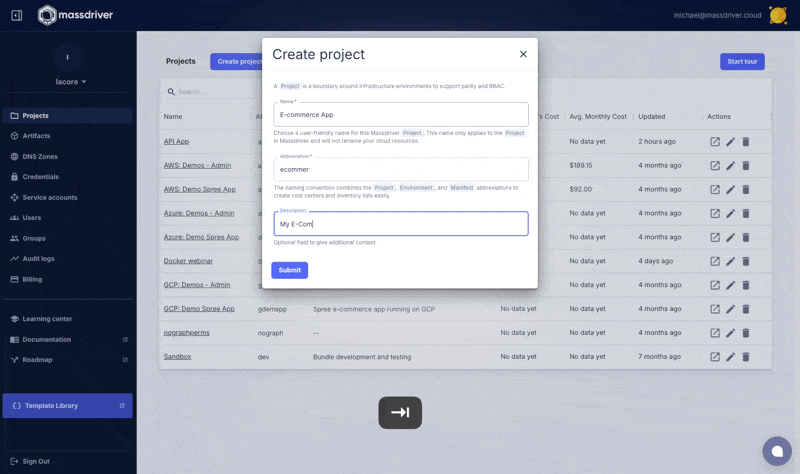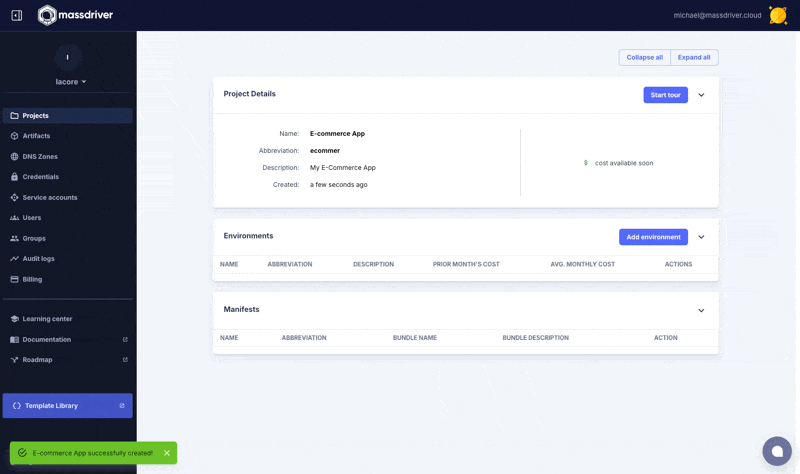
Next navigate to projects and create a new project named Example. A project is a parity boundary and used to replicate infrastructure and applications between environments like application environments (staging, production) and/or regions (us-west-1, us-west-2, or prod us west 2).
 .
.
Add an environment named Staging.
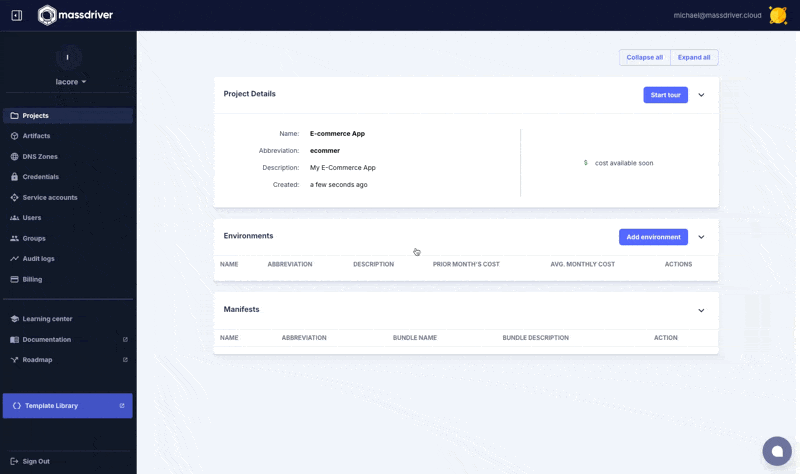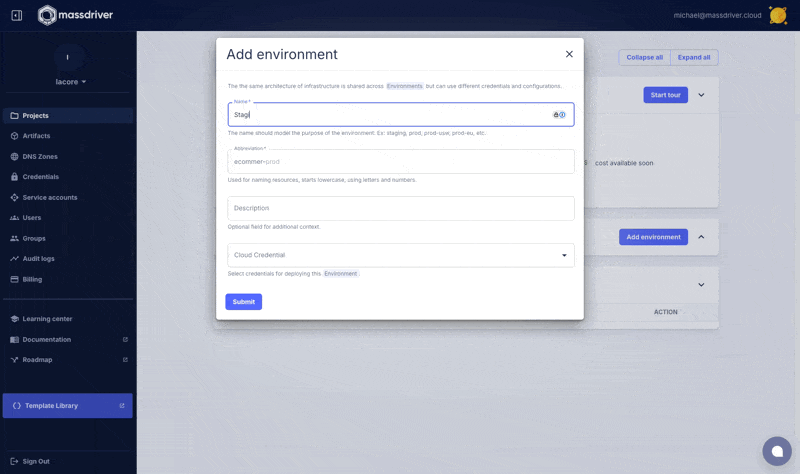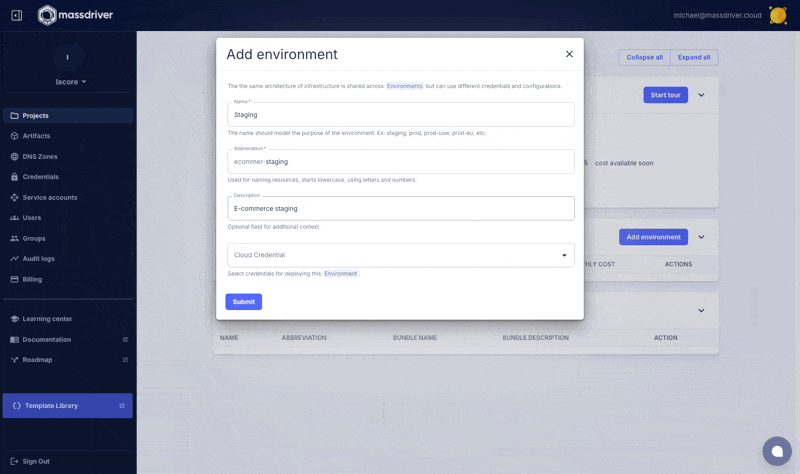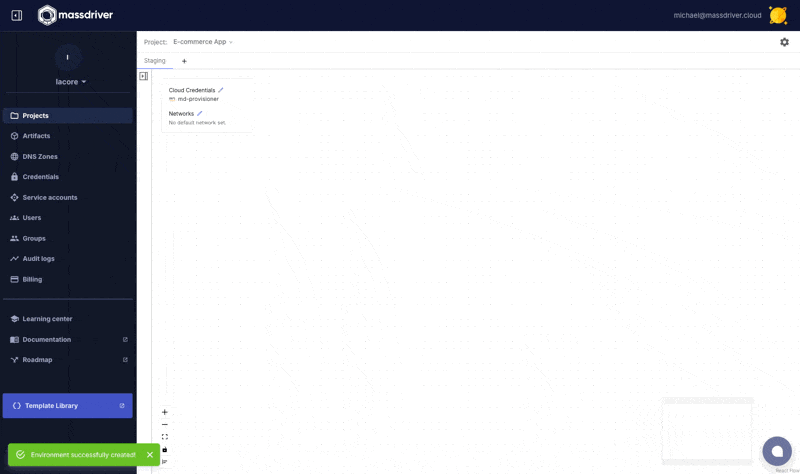
Attach the credential you created in the Create environment screen.
Design and deploy infrastructure for your application:
If you followed the guide in the previous section your application will depend on a Kubernetes Cluster and PostgreSQL.
Add and connect the following resources from the bundle sidebar. To expand the sidebar click the "package" icon.
You'll need to add:
- massdriver/aws-vpc
- massdriver/aws-eks-cluster
- massdriver/aws-rds-postgres or massdriver/aws-aurora-serverless-postgres
After adding each to the canvas, click on the package. Feel free to fine tune the configuration, but if you are new to cloud infrastructure the Configuration Presets are a great way to get started quickly. Select a preset like Development and then click Deploy.
The artifact system in Massdriver (the boxes you connect lines to) shares common types between bundles to make it possible to swap between different infrastructure bundles that provide the same functionality.
In this example you could use massdriver/aws-rds-postgres, massdriver/aws-aurora-serverless-postgres, or a version of PostgreSQL running on Kubernetes.
Once all of your infrastructure has booted up, you can add and connect your application: YOUR_ORG_PREFIX/k8s-phoenix-chat-example.
You can now click configure and set your values. You can set any values here that makes sense for your application. A publicly hosted docker repository can be used: massdriver/cloud/phoenix-chat-example.
Once your application has been configured and connected, it can also be deployed from our CLI.
The deploy command expects the package name in the format of foo-bar-baz. If you followed the above example it will be example-staging-phoenixchat. If you can't remember the name of your application, mouse over its human-friendly name in the UI and it will be displayed.
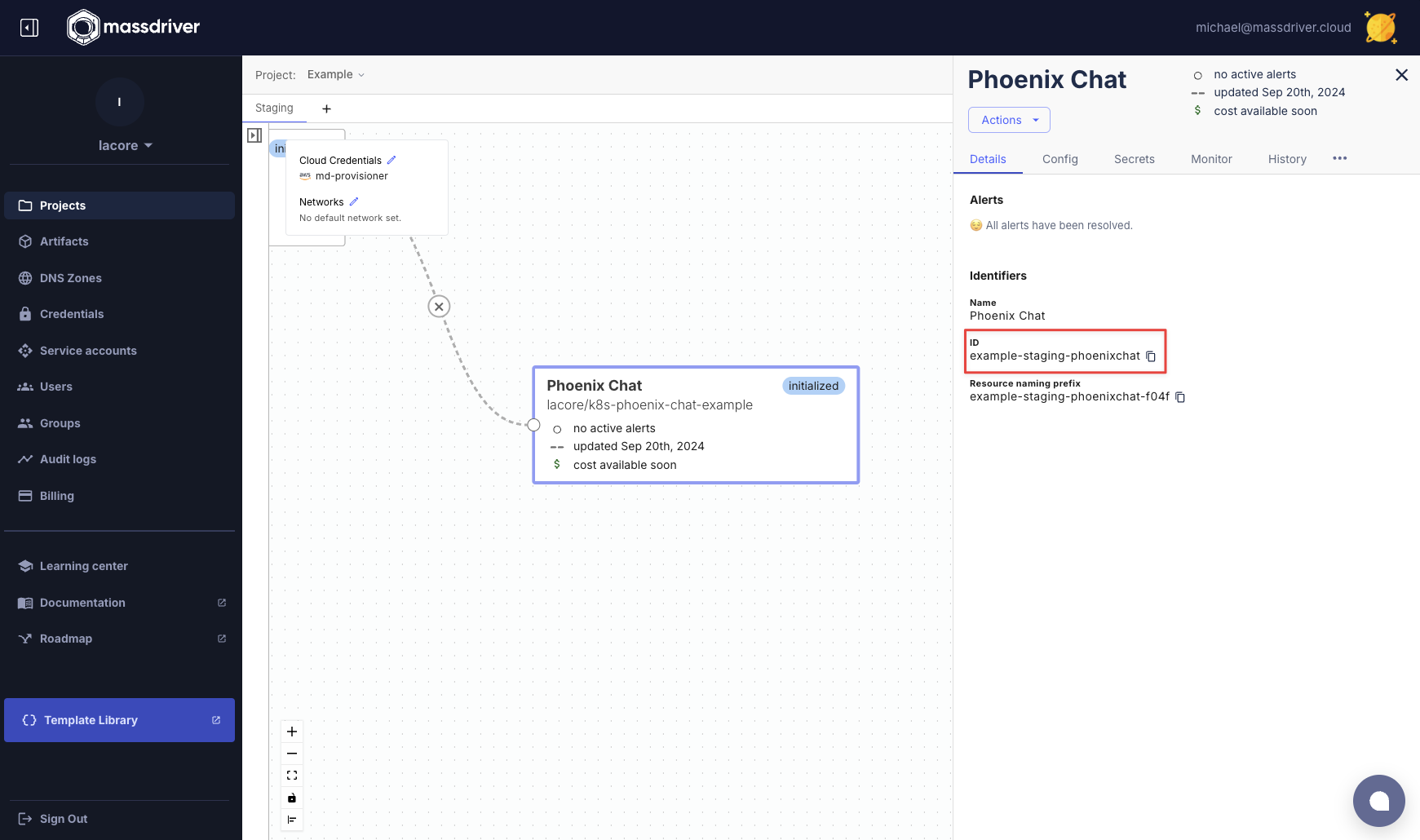
mass deploy can be added to your CI/CD pipeline to trigger deployments to your Kubernetes cluster.
export MASSDRIVER_ORG_ID=FOO
export MASSDRIVER_API_KEY=BAR
mass deploy example-staging-phoenixchat
Your Organization ID can be found by hovering over your org name in the sidebar: